INM-755 Cannabinol (CBN) Cream
INM-755 is a cannabinol topical cream which has been under development for the treatment of epidermolysis bullosa. INM-755 cream for EB is the first cannabinol formulation to be tested in clinical trials as a therapeutic product.
Phase 2 clinical trial of INM-755 cannabinol cream completed
InMed has completed a Phase 2 clinical trial of INM-755 (cannabinol) cream studying the safety and efficacy in Epidermolysis Bullosa (EB). Results from the Phase 2 clinical trial showed a positive indication of enhanced anti-itch activity for INM-755 cannabinol cream versus the control cream alone in an exploratory clinical evaluation. The results for non-wound itch were not statistically significant in this small trial due, in part, to the clinically important anti-itch effect of the underlying control cream.
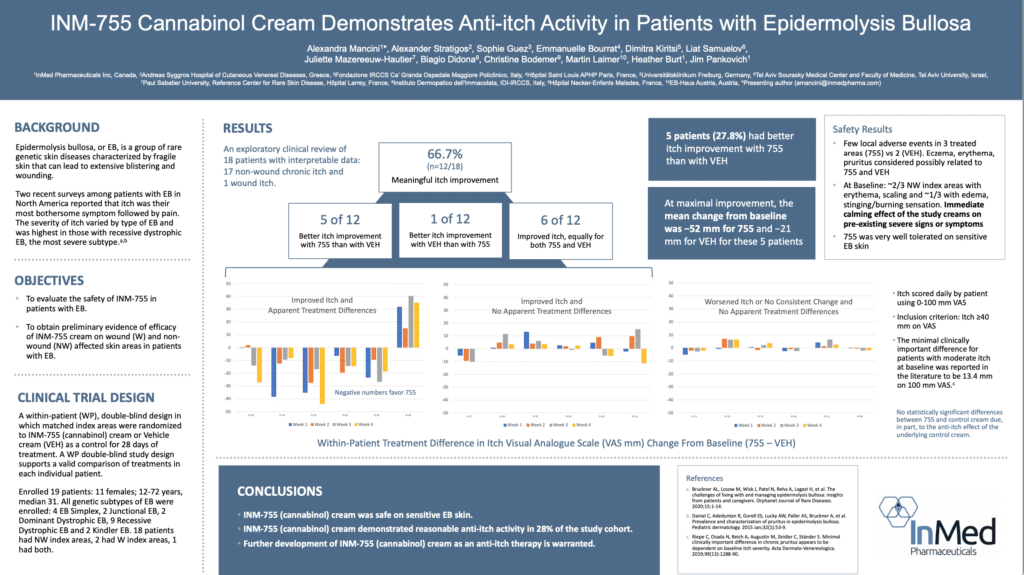
The Phase 2 trial enrolled a total of 19 patients. The purpose of the Phase 2 trial was to evaluate the safety of INM-755 CBN cream, which consists of the control cream plus the active pharmaceutical ingredient CBN, and obtain preliminary evidence of efficacy in treating symptoms and healing wounds over a 28-day period in patients with EB. All four subtypes of inherited EB, including EB Simplex, Dystrophic EB, Junctional EB, and Kindler Syndrome were accepted into the Phase 2 trial. The Phase 2 trial used a within-patient, double-blind design whereby matched index areas were randomized to INM-755 CBN cream or control cream.
InMed will pursue strategic partnership opportunities for INM-755 in epidermolysis bullosa and other itch-related skin conditions.
InMed presents Phase 2 clinical study results at 12th World Congress on Itch
InMed’s abstract “INM-755 cannabinol cream demonstrates anti-itch activity in patients with epidermolysis bullosa” describing the Phase 2 clinical study of investigational drug INM-755 cannabinol (CBN) cream for the treatment of symptoms in patients with epidermolysis bullosa, was accepted as an oral presentation at the 12th World Congress on Itch (WCI), held in Miami on November 5-7, 2023.
CBN demonstrates an excellent safety profile
InMed’s Phase 1 and 2 clinical trials of INM-755 demonstrated that CBN is safe and well-tolerated. In the Phase 2 trial, there were no serious drug-related adverse events (“AEs”) and there were no withdrawals from treatment. Moderate headaches in one study participant were the only systemic AEs deemed ‘possibly related’ to study drug. Very few local AEs were reported in the treatment areas; they were transient and resolved without cessation of treatment. The Phase 2 trial indicated that INM-755 CBN cream was very well tolerated on sensitive EB skin.
Results from two Phase 1 clinical studies of INM-755 cream in healthy volunteers treated for 14 days indicated that INM-755 cream was safe and well-tolerated on intact skin as well as open epidermal wounds, caused no systemic or serious adverse effects, and there were no subject withdrawals due to adverse events.
In addition, InMed conducted several preclinical safety pharmacology and toxicology studies using CBN at very high doses that achieved systemic exposure (blood levels) hundreds of times higher than what is expected to occur with topical dosing in humans. No adverse events were seen on central nervous system (CNS) function in a rigorous and extensive evaluation of CNS effects; 108 aspects of behavior posture, gait, and movement were assessed.
Preclinical studies show CBN potential in managing symptoms of EB as well as improving skin integrity in a subset of EB patients
InMed completed extensive safety pharmacology and toxicology studies of CBN and INM-755 cream that demonstrated promising results and supported advancing the compound into clinical trials.
In preclinical pharmacology studies, CBN demonstrated activity in reducing markers of inflammation and pain. It also upregulated expression of a type of keratin (keratin 15, or K15), which might lead to improved skin integrity and reduced blister formation in EB simplex (EBS) patients with mutations of another keratin (keratin 14, or K14). Its anti-inflammatory activity may be beneficial in healing chronic wounds where healing has been prevented by prolonged inflammation.
INM-755 cream is the first cannabinol formulation under therapeutic development in clinical trials
Rare cannabinoid CBN is the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) in INM-755. INM-755 cream is the first CBN formulation being studied in clinical trials as a potential therapeutic to treat disease.
In addition to the pharmaceutical program in epidermolysis bullosa, CBN is also the API in InMed’s glaucoma eye drop formulation (INM-088) which is being studies in preclinical testing.
What is epidermolysis bullosa?
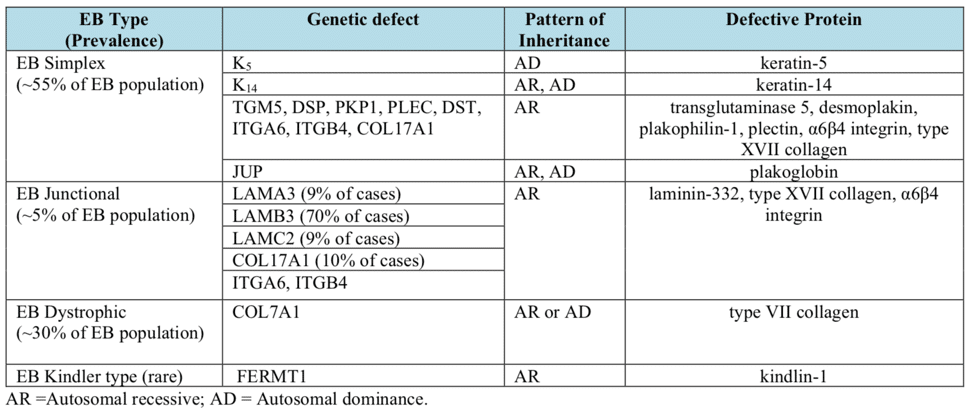
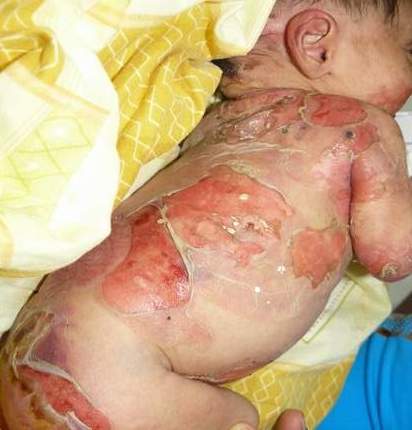
Epidermolysis bullosa, or EB, is a rare genetic skin disease characterized by fragile skin that can lead to extensive blistering and wounding. It is a painful and often debilitating disease that affects skin and mucous membranes, particularly of the gastrointestinal tract, genitourinary and respiratory systems. According to debra of America, a non-profit organization supporting the EB community, EB affects 1 out of 20,000 births in the United States – approximately 200 children a year are born with EB. The disease has no cure and all current treatments are directed towards symptom relief.